 The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas,
The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas,
as part of the eSMA project.
The eSMA (expanded Submillimeter Array) is a project
which synthesizes the signals detected with
the CSO 10.4 meter
antenna, the JCMT 15
meter antenna, and eight 6-meter SMA
antennas. The
eSMA
allows us to improve sensitivities and spatial resolution significantly
(almost twice improved) compared
with the
capability of the SMA itself.
The eSMA testing was done under fair weather
condition
(tau225 ~ 0.1-0.15) on 12 Dec 2005,
following the first engineering run on 6th of December 2005. For
this run, 8 antennas were used
(six SAO SMA antennas, CSO and JCMT). We
observed a lot of quasars to determine baseline
parameters
of the CSO. This experiment was interesting particularly
because z (one of the baseline
parameters) was not determined yet for the CSO antenna. In
this experiment, the CSO is named as
antenna 9. Note that antenna 1 through 6 are for the SMA
antennas, antenna 10 is JCMT. No fringes
were detected with antenna 10
because of some tuning issue JCMT had on the day
unfortunately.
Figure 2
is the array configuration of the SMA
antennas. They were in the compact configuration this time.
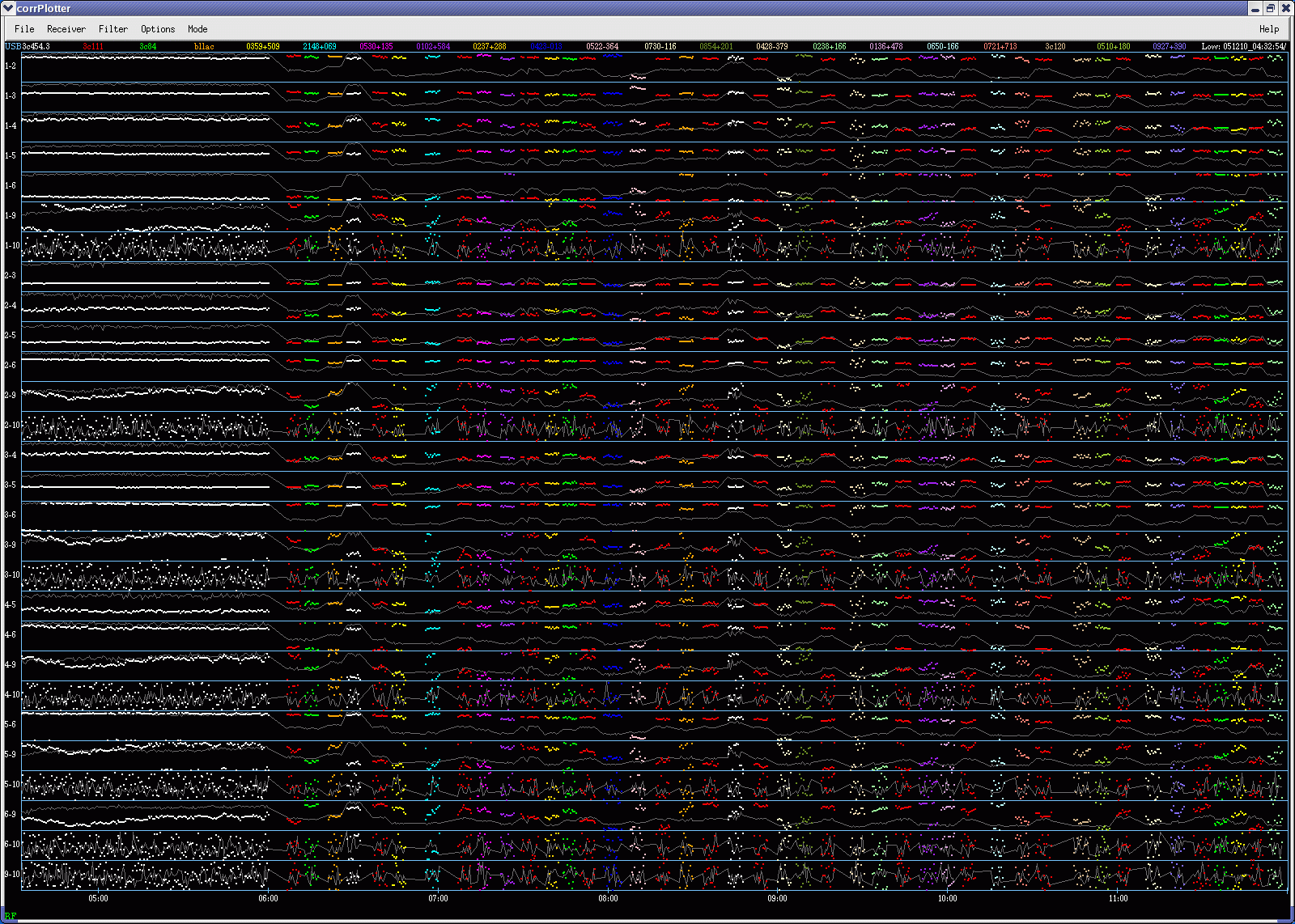
Figure 1. Phase (dots in various colors) and amplitude (narrow
grey lines) variations of fringes on all baselines towards
various quasars measured in an eSMA experiment done in December
2005. Numbers noted in
left side (such as 1-2)
indicates the baseline between the two antennas. The CSO
telescope (assigned as antenna 9)
obtained clear
fringes with
all
the SMA antennas joined in this experiment. (Fringes are detected
if dots are clustering. ) This is one of the plots
which the SMA team develops for the regular interferometric
observations.
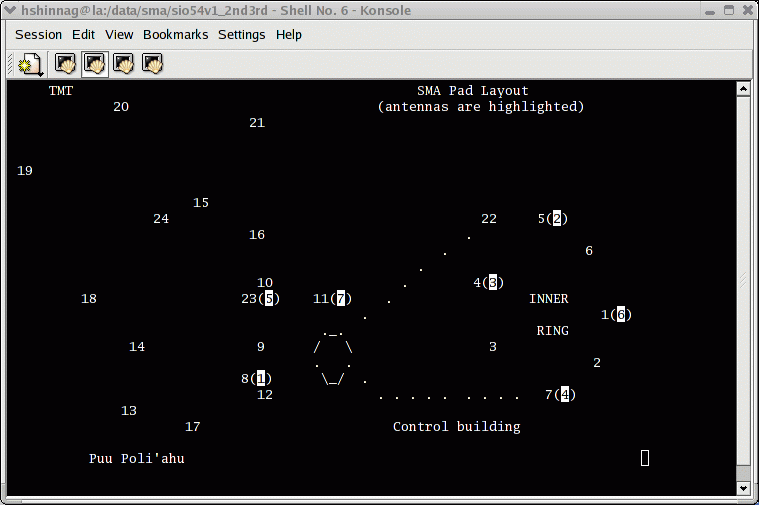
Figure 2. The array configuration of the SMA antennas in the experiment
done on
12 Dec 2005. (Note that antenna 7
on pad 11 did not join this experiment. ) This is one of the
plots which the SMA team develops for the regular
interferometric observations.

 The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas,
The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas, 
 The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas,
The
CSO antenna obtained fringes with SMA antennas, 

